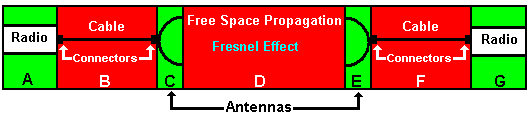
Key: Green is good, Red is bad.
Use this calculator to walk through all the factors that make up your Power Budget. The ‘Power Budget’ is the the total power being output from the wireless system and is the sum of:
- PLUS Radio Transmit Power (A above)
- MINUS cables and connectors losses (B above)
- PLUS antenna gain (C above).
Enter one parameter in each column (or leave blank) depending on what you know and the calculator will supply the appropriate conversions automatically. Up to 2 decimal places may be entered as 0.xx or .xx.
Note: Connector loss is generally small UNLESS you’ve got lots of ’em in which case you are probably in trouble anyway, or your cable is VERY short. Just leave the line blank if you are feeling lazy.
Calculations and equations used.